What must happen to the Blastocyst before it becomes an embryo?
In Vitro Fertilization
The NYU Langone Fertility Center has a world-renowned in vitro fertilization (IVF) plan known for its high pregnancy success rates. IVF is the most efficient way for couples to achieve pregnancy when they are experiencing trouble conceiving.
In order for pregnancy to naturally occur, sperm must travel through the uterus to ane of the fallopian tubes, where it fertilizes an egg. The resulting embryo must exist of good quality in guild for implantation to occur.
While the process sounds uncomplicated, there are multiple factors that tin can stop these steps from happening, such as a low sperm count, a compromised or blocked fallopian tube, a damaged or diseased uterus, or suboptimal egg production or quality. When the sperm and egg are unable to meet on their own, or egg or sperm quality is lower than desired, IVF may exist an selection.
During IVF, eggs are retrieved from the ovaries—or donor eggs may be used—and fertilized with sperm acquired either from a partner or a donor. The resulting embryo is inserted into the uterus, where it ideally implants and creates a pregnancy.
People having IVF must attend an on-site orientation session conducted by our nursing staff before beginning treatment. Partners are encouraged to nourish this session also. In improver to attending an in-person session, you can too view our orientation program.
While every woman's cycle is unique, hither is a full general overview of the IVF process.
Stride One: Ovulation Consecration
During a typical menstrual cycle, the ovaries release one egg each month. In preparation for IVF, fertility drugs, called gonadotropins, are self-administered daily to stimulate the ovaries to mature numerous eggs in the calendar month of the treatment cycle. If more eggs are matured, more than can exist harvested and used. Almost often, this improves the chances of fertilization and, ultimately, pregnancy.
Step Two: Egg Retrieval (Oocyte Retrieval)
When the eggs, also known as oocytes, are ready to be retrieved from the body, a process is performed at the Fertility Center using mild sedation. The md—with the aid of ultrasound visualization—guides a needle through the vagina wall and into the ovaries. An anesthesiologist is present for all procedures.
After the eggs are retrieved, they are fertilized with sperm in the embryology laboratory. Success rates vary depending on a person's historic period, response to the medication, and the quality of the eggs and embryos produced.
As with all surgical procedures, there are risks associated with egg retrieval that should be discussed with your doctor.
Step Three: Fertilization in the Lab
When the eggs go far in the embryology lab, our staff analyzes them for maturity and and so places the eggs into an incubator that has an environment similar to the one inside the body. In most cases, sperm is combined with the eggs and fertilization occurs naturally. In situations where low sperm count or low sperm motion (movement) is a factor, a single sperm is injected direct into each mature egg in a process chosen intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
Once the egg and sperm are combined, it takes approximately eighteen hours to determine whether fertilization has occurred and another ii to 4 days to establish whether the embryo is optimally developing. The embryos well-nigh frequently stay in the laboratory for a full of 5 days.
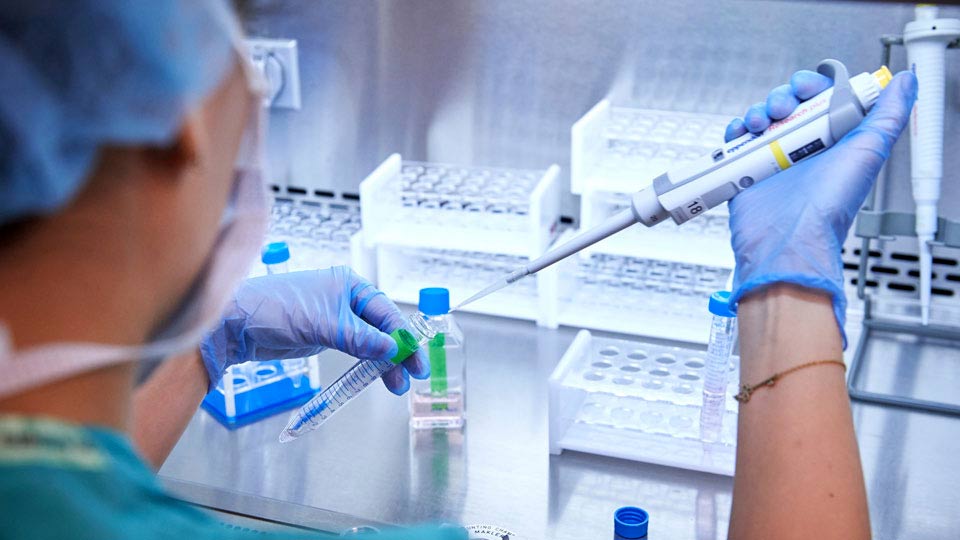
An embryologist pipettes a sample into a examination tube at the Fertility Center'southward fertility lab.
In fourscore percent of our current patient cycles, preimplantation genetic screening (PGS) of the created embryos is performed at this phase to assess the chromosomal integrity of the created embryos.
Footstep Four: Embryo Transfer
In preparation for the embryo transfer, the doctor discusses the number of embryos produced besides as the quality of each. Grading is a tool physicians and embryologists use to determine which embryos to transfer and when. One of the Fertility Center's goals is to limit the number of embryos transferred in order to limit the number of multiple births. In more than sixty percent of the embryo transfers we perform, only a single embryo is placed into the uterus.
Embryo transfer is a elementary technique, and anesthesia or sedation is rarely required. A long, thin catheter containing the agreed upon number of embryos, forth with a small corporeality of fluid, is passed through the cervix into the uterus, where the embryo or embryos are released. An abdominal ultrasound is simultaneously performed to ensure optimal placement in the uterus.
Following the embryo transfer, limitation of rigorous concrete activeness is recommended for several days.
After an Embryo Transfer
Afterwards a blastocyst embryo transfer is completed, information technology takes about nine days earlier a pregnancy can be detected. During the days after a transfer, the post-obit happens to the embryo:
- Day 1: The blastocyst begins to hatch out of its trounce.
- Solar day 2: The blastocyst continues to hatch out of its shell and begins to attach itself to the uterus.
- Solar day iii: The blastocyst attaches deeper into the uterine lining, beginning implantation.
- Twenty-four hour period 4: Implantation continues.
- Day 5: Implantation is complete. Cells that eventually get the placenta and fetus have begun to develop.
- Day 6: Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), the hormone that signals a developing pregnancy, starts to enter the blood stream.
- Days 7 and eight: Fetal development continues and hCG continues to be secreted.
- Mean solar day 9: Levels of hCG are now high enough in maternal blood to detect a pregnancy using a claret test.
Embryo Freezing or Cryopreservation
Embryos are cryopreserved, or frozen, for multiple reasons. The traditional IVF process often results in more than embryos than tin can be transferred into the uterus in 1 wheel. If the non-transferred embryos are of acceptable quality, they can be frozen and stored for hereafter apply. Embryos are likewise frozen subsequently preimplantation genetic screening has been performed. In add-on, embryo freezing is a way for people to delay childrearing until a more than appropriate time in their lives.
Cryopreservation of embryos reduces the demand for repeated ovarian stimulation. Instead of IVF, hereafter cycles can exist embryo transfers, which are less difficult, both physically and financially.
Circuitous Types of IVF
At the Fertility Center, we consider IVF to be "circuitous" if prior attempts have been unsuccessful, if sperm counts or motion are severely low, or if the quality of the resulting embryos has been poor. This last reason may be due to many factors; most commonly it'south related to advanced maternal historic period, merely information technology may too be due to endocrine disorders, such as polycystic ovary syndrome. When very severe male person infertility requires surgical extraction of sperm, this is also considered to exist a complex blazon of IVF.
Contact United states of america
To schedule an appointment, delight telephone call the private doctor'southward role phone line, the center's chief number at 212-263-8990, or fill out our date asking class.
cardenasevied1952.blogspot.com
Source: https://nyulangone.org/locations/fertility-center/in-vitro-fertilization-egg-freezing-embryo-banking/in-vitro-fertilization
0 Response to "What must happen to the Blastocyst before it becomes an embryo?"
Post a Comment